Difference between revisions of "Docker"
imported>Plittlefield |
Plittlefield (talk | contribs) (→Tweaks) |
||
| Line 1,442: | Line 1,442: | ||
$wgArticlePath = "/wiki/$1"; | $wgArticlePath = "/wiki/$1"; | ||
$wgUsePathInfo = true; | $wgUsePathInfo = true; | ||
| + | |||
| + | File uploads... | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Manual:Configuring_file_uploads | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://kindalame.com/2020/11/25/self-hosting-mediawiki-with-docker/ | ||
==== Importing ==== | ==== Importing ==== | ||
Revision as of 14:13, 21 May 2021
Introduction
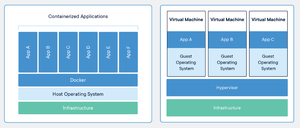
Docker is a set of platform as a service products that use OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. Containers are isolated from one another and bundle their own software, libraries and configuration files but they can communicate with each other through well-defined channels.
https://www.docker.com - Official Web Site.
https://hub.docker.com - Official Repository of Container Images.
It was originally developed for programmers to test their software but has now become a fully fledged answer to running servers in mission critical situations.
Each container has a mini operating system plus the software needed to run the program you want, and no more.
All of the 'hard work' for a piece of software has been 'done for you' and the end result is starting a program with one command line.
For example, the WordPress image contains the LAP part of LAMP (Linux + Apache + PHP) all configured and running.
Images
Installation
Engine
This will remove the old version of 'Docker' and install the new version 'Docker CE'...
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io sudo apt-get -y install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add - sudo apt-key fingerprint 0EBFCD88 sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" sudo apt-get -y install docker-ce sudo docker run hello-world
https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/docker-ce/ubuntu/#install-docker-ce-1
Compose
curl -I -s "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/latest" | grep 'location:' | sed 's/^.*[/]//'
Check the latest version of 'Docker Compose' and edit the following command...
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose /usr/local/bin/docker-compose --version
https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/#install-compose
Usage
Statistics
docker stats docker stats --no-stream
System information
docker system info
Run container
docker run hello-world
List containers
docker container ls docker container ls -a
List container processes
docker ps
docker ps --format "table {{.ID}}\t{{.Names}}\t{{.Image}}\t{{.Ports}}\t{{.Status}}"
List container names
docker ps --format '{{.Names}}'
docker ps -a | awk '{print $NF}'
List volumes
docker volume ls docker volume ls -f dangling=true
List networks
docker network ls
Information about container
docker container inspect container_name or id
Stop container
docker stop container_name
Delete container
docker rm container_name
Delete volumes
docker volume rm volume_name
Delete all unused volumes
docker volume prune
Delete all unused networks
docker network prune
Prune everything unused
docker system prune
Upgrade a stack
docker-compose pull docker-compose up -d
BASH Aliases for use with Docker commands
alias dcd='docker-compose down' alias dcr='docker-compose restart' alias dcu='docker-compose up -d' alias dps='docker ps'
Volumes
Multiple Containers
Use volumes which are bind mounted from the host filesystem between multiple containers.
First, create the volume bind mounted to the folder...
docker volume create --driver local --opt type=none --opt device=/path/to/folder --opt o=bind volume_name
Then, use it in your docker compose file...
services:
ftp.domain.uk-nginx:
image: nginx
container_name: ftp.domain.uk-nginx
expose:
- "80"
volumes:
- ./data/etc/nginx:/etc/nginx
- ftp.domain.uk:/usr/share/nginx:ro
environment:
- VIRTUAL_HOST=ftp.domain.uk
networks:
default:
external:
name: nginx-proxy-manager
volumes:
ftp.domain.uk:
external: true
Using volumes in Docker Compose
Networks
Create your network...
docker network create existing-network
Use it in your docker-compose.yml file...
services:
service_name:
image: image_name:latest
restart: always
networks:
- existing-network
networks:
existing-network:
external: true
https://poopcode.com/join-to-an-existing-network-from-a-docker-container-in-docker-compose/
Management
Cleaning Space
Over the last month, a whopping 14Gb of space was being used by /var/lib/docker/overlay2/ and needed a way to safely remove unused data.
Check your space usage...
du -mcsh /var/lib/docker/overlay2 14G /var/lib/docker/overlay2
Check what Docker thinks is being used...
docker system df TYPE TOTAL ACTIVE SIZE RECLAIMABLE Images 36 15 8.368GB 4.491GB (53%) Containers 17 15 70.74MB 286B (0%) Local Volumes 4 2 0B 0B Build Cache 0 0 0B 0B
Clean...
docker system prune docker image prune --all
Check again...
du -mcsh /var/lib/docker/overlay2 9.4G /var/lib/docker/overlay2 docker system df TYPE TOTAL ACTIVE SIZE RECLAIMABLE Images 13 13 4.144GB 144MB (3%) Containers 15 15 70.74MB 0B (0%) Local Volumes 4 2 0B 0B Build Cache 0 0 0B 0B
...job done.
Portainer
https://github.com/portainer/portainer
https://hub.docker.com/r/portainer/portainer-ce
Monitoring
CTop
Press the Q key to stop it...
docker run -ti --name ctop --rm -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock wrfly/ctop:latest
Docker Stats
docker stats
Gotchas
https://sosedoff.com/2016/10/05/docker-gotchas.html
Applications
I have set up my docker containers in a master docker directory with sub-directories for each stack.
docker
|-- backups
`-- stacks
|-- bitwarden
| `-- bwdata
|-- grafana
| `-- data
|-- mailserver
| `-- data
|-- nginx-proxy-manager
| `-- data
`-- portainer
`-- data
Backups
https://github.com/alaub81/backup_docker_scripts
Updates
Tracking
Watchtower
A process for automating Docker container base image updates.
With watchtower you can update the running version of your containerized app simply by pushing a new image to the Docker Hub or your own image registry. Watchtower will pull down your new image, gracefully shut down your existing container and restart it with the same options that were used when it was deployed initially.
First Time Run Once Check Only
This will run and output if there are any updates them stop and remove itself...
docker run --name watchtower -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock containrrr/watchtower --run-once --debug --monitor-only --rm
Automated Scheduled Run Daily
This will start the container and schedule a check at 4am every day...
~/watchtower/docker-compose.yml
version: "3"
services:
watchtower:
image: containrrr/watchtower
container_name: watchtower
restart: always
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
environment:
- TZ=${TZ}
- WATCHTOWER_DEBUG=true
- WATCHTOWER_MONITOR_ONLY=false
- WATCHTOWER_CLEANUP=true
- WATCHTOWER_LABEL_ENABLE=false
- WATCHTOWER_NOTIFICATIONS=email
- WATCHTOWER_NOTIFICATION_EMAIL_FROM=${EMAIL_FROM}
- WATCHTOWER_NOTIFICATION_EMAIL_TO=${WATCHTOWER_EMAIL_TO}
- WATCHTOWER_NOTIFICATION_EMAIL_SERVER=${SMTP_SERVER}
- WATCHTOWER_NOTIFICATION_EMAIL_SERVER_PORT=${SMTP_PORT}
- WATCHTOWER_NOTIFICATION_EMAIL_SERVER_USER=${SMTP_USER}
- WATCHTOWER_NOTIFICATION_EMAIL_SERVER_PASSWORD=${SMTP_PASSWORD}
- WATCHTOWER_SCHEDULE=0 0 4 * * *
https://containrrr.dev/watchtower/
https://containrrr.dev/watchtower/arguments/#without_updating_containers
https://github.com/containrrr/watchtower
https://www.the-digital-life.com/watchtower/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5lP_pdjcVMo
Updating
You can either ask Watchtower to update the containers automatically for you, or do it manually.
Manually updating when using docker-compose...
cd /path/to/docker/stack/ docker-compose stop docker-compose pull docker-compose start
Bitwarden
~/bitwardenrs/docker-compose.yml
version: "2"
services:
bitwardenrs:
image: bitwardenrs/server:latest
container_name: bitwardenrs
volumes:
- ./data:/data/
ports:
- 8100:80
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- TZ=Europe/London
#- SIGNUPS_ALLOWED=false
#- INVITATIONS_ALLOWED=false
#- WEB_VAULT_ENABLED=false
networks:
default:
external:
name: nginx-proxy-manager
Uncomment the extra security # lines after you have signed up, imported your old vault and set up your phone app and browsers, etc.
docker-compose down docker-compose up -d
Check that the Bitwarden container environment has all the variables...
docker exec -it bitwardenrs env | sort HOME=/root HOSTNAME=e5f327deb4dd INVITATIONS_ALLOWED=false PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin ROCKET_ENV=staging ROCKET_PORT=80 ROCKET_WORKERS=10 SIGNUPS_ALLOWED=false TERM=xterm TZ=Europe/London WEB_VAULT_ENABLED=false
... and then refresh your web vault page to see it see "404: Not Found" :-)
InfluxDB
You can have InfluxDB on its own but there is little point without something to view the stats so you might as well include InfluxDB in the Grafana stack and start both at the same time... see below :-)
Grafana
Here is a stack in docker-compose which starts both containers in their own network so they can talk to one another. I have exposed ports for InfluxDB and Grafana to the host so I can use them from the internet.
Obviously, put your firewall in place and change the passwords below!
~/grafana/docker-compose.yml
version: "3"
services:
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana
container_name: grafana
restart: always
networks:
- grafana-influxdb-network
ports:
- 3000:3000
volumes:
- ./data/grafana:/var/lib/grafana
environment:
- INFLUXDB_URL=http://influxdb:8086
depends_on:
- influxdb
influxdb:
image: influxdb:1.8.4
container_name: influxdb
restart: always
networks:
- grafana-influxdb-network
ports:
- 8086:8086
volumes:
- ./data/influxdb:/var/lib/influxdb
environment:
- INFLUXDB_DB=grafana
- INFLUXDB_USER=grafana
- INFLUXDB_USER_PASSWORD=password
- INFLUXDB_ADMIN_ENABLED=true
- INFLUXDB_ADMIN_USER=admin
- INFLUXDB_ADMIN_PASSWORD=password
- INFLUXDB_URL=http://influxdb:8086
networks:
grafana-influxdb-network:
external: true
After this, change your Telegraf configuration to point to the new host and change the database it uses to 'grafana'.
NGiNX Proxy Manager
Provide users with an easy way to accomplish reverse proxying hosts with SSL termination that is so easy a monkey could do it.
- Set up your host
- Add a proxy to point to the host (in Docker this will be the 'name' and the port)
- Go to http://yourhost
https://github.com/jc21/nginx-proxy-manager
Create the Docker network...
sudo -i docker network create nginx-proxy-manager
/root/stacks/nginx-proxy-manager/docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
app:
image: 'jc21/nginx-proxy-manager:latest'
container_name: nginx-proxy-manager_app
restart: always
networks:
- nginx-proxy-manager
ports:
- '80:80'
- '81:81'
- '443:443'
environment:
TZ: "Europe/London"
DB_MYSQL_HOST: "db"
DB_MYSQL_PORT: 3306
DB_MYSQL_USER: "npm"
DB_MYSQL_PASSWORD: "npm"
DB_MYSQL_NAME: "npm"
volumes:
- ./data:/data
- ./data/letsencrypt:/etc/letsencrypt
depends_on:
- db
db:
image: 'jc21/mariadb-aria:latest'
container_name: nginx-proxy-manager_db
restart: always
networks:
- nginx-proxy-manager
environment:
TZ: "Europe/London"
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: 'npm'
MYSQL_DATABASE: 'npm'
MYSQL_USER: 'npm'
MYSQL_PASSWORD: 'npm'
volumes:
- ./data/mysql:/var/lib/mysql
networks:
nginx-proxy-manager:
external: true
Reset Password
docker exec -it nginx-proxy-manager_db sh mysql -u root -p npm select * from user; delete from user where id=1; quit; exit
Custom SSL Certificate
You can add a custom SSL certificate to NPM by saving the 3 parts of the SSL from Let's Encrypt...
- privkey.pem
- cert.pem
- chain.pem
...and then uploading them to NPM.
Updating
docker-compose pull docker-compose up -d
NGiNX
Quick Container
Run and delete everything afterwards (press CTRL+C to stop it)...
docker run --rm --name test.domain.org-nginx -e VIRTUAL_HOST=test.domain.org nginx
Run and detach and use a host folder to store the web pages and keep the container afterwards...
docker run --name test.domain.org-nginx -e VIRTUAL_HOST=test.domain.org -v /some/content:/usr/share/nginx/html:ro -d nginx
Run and detach and connect to a specific network (like nginx-proxy-manager) and use a host folder to store the web pages and keep the container afterwards...
docker run --name test.domain.org-nginx --network nginx-proxy-manager -e VIRTUAL_HOST=test.domain.org -v /some/content:/usr/share/nginx/html:ro -d nginx
Check the logs and always show them (like tail -f)...
docker logs test.domain.org-nginx -f
Load Balancer
This is a simple exmaple test to show multiple backend servers answering web page requests.
docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
# The load balancer
nginx:
image: nginx:1.16.0-alpine
volumes:
- ./nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:ro
ports:
- "80:80"
# The web server1
server1:
image: nginx:1.16.0-alpine
volumes:
- ./server1.html:/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
# The web server2
server2:
image: nginx:1.16.0-alpine
volumes:
- ./server2.html:/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
nginx.conf
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
upstream app_servers { # Create an upstream for the web servers
server server1:80; # the first server
server server2:80; # the second server
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://app_servers; # load balance the traffic
}
}
}
https://omarghader.github.io/docker-compose-nginx-tutorial/
Proxy
This is very cool and allows you to run multiple web sites on-the-fly.
The container connects to the system docker socket and watches for new containers using the VIRTUAL_HOST environment variable.
Start this, then add another container using the VIRTUAL_HOST variable and the proxy container will change its config file and reload nginx to serve the web site... automatically.
Incredible.
~/nginx-proxy/docker-compose.yml
version: "3"
services:
nginx-proxy:
image: jwilder/nginx-proxy
container_name: nginx-proxy
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/tmp/docker.sock:ro
networks:
default:
external:
name: nginx-proxy
Normal
When using the nginx-proxy container above, you can just spin up a virtual web site using the standard 'nginx' docker image and link it to the 'nginx-proxy' network...
docker run -d --name nginx-website1.uk --expose 80 --net nginx-proxy -e VIRTUAL_HOST=website1.uk nginx
To use the host filesystem to store the web page files...
docker run -d --name nginx-website1.uk --expose 80 --net nginx-proxy -v /var/www/website1.uk/html:/usr/share/nginx/html:ro -e VIRTUAL_HOST=website1.uk nginx
In Docker Compose, it will look like this...
~/nginx/docker-compose.yml
version: "3"
services:
nginx-website1.uk:
image: nginx
container_name: nginx-website1.uk
expose:
- "80"
volumes:
- /var/www/website1.uk/html:/usr/share/nginx/html:ro
environment:
- VIRTUAL_HOST=website1.uk
networks:
default:
external:
name: nginx-proxy
Multiple Virtual Host Web Sites
~/nginx/docker-compose.yml
version: "3"
services:
nginx-website1.uk:
image: nginx
container_name: nginx-website1.uk
expose:
- "80"
volumes:
- /var/www/website1.uk/html:/usr/share/nginx/html:ro
environment:
- VIRTUAL_HOST=website1.uk
nginx-website2.uk:
image: nginx
container_name: nginx-website2.uk
expose:
- "80"
volumes:
- /var/www/website2.uk/html:/usr/share/nginx/html:ro
environment:
- VIRTUAL_HOST=website2.uk
networks:
default:
external:
name: nginx-proxy
Viewing Logs
docker-compose logs nginx-website1.uk docker-compose logs nginx-website2.uk
Proxy Manager
This is a web front end to manage 'nginx-proxy', where you can choose containers and create SSL certificates etc.
https://cyberhost.uk/npm-setup/
Various
https://hub.docker.com/_/nginx
https://blog.ssdnodes.com/blog/host-multiple-websites-docker-nginx/
https://github.com/nginx-proxy/nginx-proxy
WordPress
https://hub.docker.com/_/wordpress/
PHP File Uploads Fix
Create a new PHP configuration file, and name it docker-uploads.ini. Add the following configuration then save the changes.
# Allow HTTP file uploads file_uploads = On # Maximum size of an uploaded file upload_max_filesize = 64M # Maximum size of form post data post_max_size = 64M
Update the docker-compose.yml to bind the docker-uploads.ini to the wordpress container and then restart the WordPress container.
volumes: - ./data/config/docker-uploads.ini:/usr/local/etc/php/conf.d/docker-uploads.ini
WordPress Clone
Create your A record in DNS using AWS Route 53 CLI...
cli53 rrcreate domain.co.uk 'staging 300 A 123.456.78.910'
Create your docker folder for the cloned staging test web site...
mkdir -p ~/docker/stacks/staging.domain.co.uk/data/{db,html}
Edit your docker compose file, with 2 containers, making sure you use the same network as your Nginx Proxy Manager...
~/docker/stacks/staging.domain.co.uk/docker-compose.yml
version: "3"
services:
staging.domain.co.uk-wordpress_db:
image: mysql:5.7
container_name: staging.domain.co.uk-wordpress_db
volumes:
- ./data/db:/var/lib/mysql
restart: always
environment:
- TZ=Europe/London
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=siel6aiL
- MYSQL_DATABASE=dbname
- MYSQL_USER=dbuser
- MYSQL_PASSWORD=ru5BeoFa
staging.domain.co.uk-wordpress:
depends_on:
- staging.domain.co.uk-wordpress_db
image: wordpress:latest
container_name: staging.domain.co.uk-wordpress
volumes:
- ./data/html:/var/www/html
restart: always
environment:
- TZ=Europe/London
- VIRTUAL_HOST=staging.domain.co.uk
- WORDPRESS_DB_HOST=staging.domain.co.uk-wordpress_db:3306
- WORDPRESS_DB_NAME=dbname
- WORDPRESS_DB_USER=dbuser
- WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD=ru5BeoFa
networks:
default:
external:
name: nginx-proxy-manager
Start containers with correct settings and credentials for existing line web site (so that the docker startup script sets up the MySQL permissions)...
docker-compose up -d
Check the logs to make sure all is well...
docker logs staging.domain.co.uk-wordpress docker logs staging.domain.co.uk-wordpress_db
Copy the WordPress files to the host folder and correct ownership...
cp -av /path/to/backup_unzipped_wordpress/ ~/docker/stacks/staging.domain.co.uk/html/ chown -R www-data:www-data ~/docker/stacks/staging.domain.co.uk/html/
Copy the sql file in to the running mysql container...
docker cp db_name.sql mysql_container_name:/tmp/
Log in to the database container...
docker exec -it mysql_container_name bash
Check and if necessary, change the timezone...
date mv /etc/localtime /etc/localtime.backup ln -s /usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/London /etc/localtime date
Delete and create the database...
mysql -u root -p -e "DROP DATABASE db_name; CREATE DATABASE db_name;"
Import the database from the sql file, check and exit out of the container...
mysql -u root -p mysql_db_name < /tmp/db_name.sql mysql -u root -p -e "use db_name; show tables;" rm /tmp/db_name.sql exit
Edit the wp-config.php on your host server to match new DB_HOST and also add extra variables to be sure...
nano /path/to/docker/folder/html/wp-config.php define( 'WP_HOME', 'http://staging.domain.co.uk' ); define( 'WP_SITEURL', 'http://staging.domain.co.uk' );
Install WordPress CLI in the running container...
docker exec -it wordpress_container_name bash
Search and replace the original site url...
./wp --allow-root search-replace 'http://www.domain.co.uk/' 'http://staging.domain.co.uk/' --dry-run ./wp --allow-root search-replace 'http://www.domain.co.uk/' 'http://staging.domain.co.uk/'
Start your web browser and go to the test staging web site!
WordPress CLI
In your stack, set up the usual two DB + WordPress containers, then add a third services section for wp-cli...
version: "3"
services:
www.domain.uk-wordpress_db:
image: mysql:5.7
container_name: www.domain.uk-wordpress_db
volumes:
- ./data/db:/var/lib/mysql
restart: always
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=password
- MYSQL_DATABASE=wordpress
- MYSQL_USER=wordpress
- MYSQL_PASSWORD=password
www.domain.uk-wordpress:
depends_on:
- www.domain.uk-wordpress_db
image: wordpress:latest
container_name: www.domain.uk-wordpress
volumes:
- ./data/html:/var/www/html
expose:
- 80
restart: always
environment:
- VIRTUAL_HOST=www.domain.uk
- WORDPRESS_DB_HOST=www.domain.uk-wordpress_db:3306
- WORDPRESS_DB_USER=wordpress
- WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD=password
www.domain.uk-wordpress-cli:
image: wordpress:cli
container_name: www.domain.uk-wordpress-cli
volumes:
- ./data/html:/var/www/html
environment:
- WP_CLI_CACHE_DIR=/tmp/
- VIRTUAL_HOST=www.domain.uk
- WORDPRESS_DB_HOST=www.domain.uk-wordpress_db:3306
- WORDPRESS_DB_USER=wordpress
- WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD=password
working_dir: /var/www/html
user: "33:33"
networks:
default:
external:
name: nginx-proxy-manager
...then start it all up.
docker-compose up -d
Then, run your wp-cli commands (e.g. wp user list) on the end of a docker run command...
docker-compose run --rm www.domain.uk-wordpress-cli wp --info docker-compose run --rm www.domain.uk-wordpress-cli wp cli version docker-compose run --rm www.domain.uk-wordpress-cli wp user list docker-compose run --rm www.domain.uk-wordpress-cli wp help theme docker-compose run --rm www.domain.uk-wordpress-cli wp theme delete --all
Email Server
https://github.com/docker-mailserver/docker-mailserver
Postgrey
SpamAssassin
SpamAssassin is controlled by Amavis (a fork of MailScanner) with the user 'amavis'.
Show Bayes Database Stats
docker exec --user amavis mail.mydomain.org.uk-mailserver sa-learn --dump magic --dbpath /var/lib/amavis/.spamassassin
Learn Ham
docker exec --user amavis mail.mydomain.org.uk-mailserver sa-learn --ham --progress /var/mail/mydomain.org.uk/info/cur --dbpath /var/lib/amavis/.spamassassin
Backups
Autodiscover
Create SRV and A record entries in your DNS for the services...
$ORIGIN domain.org.uk. @ 300 IN TXT "v=spf1 mx ~all; mailconf=https://autoconfig.domain.org.uk/mail/config-v1.1.xml" _autodiscover._tcp 300 IN SRV 0 0 443 autodiscover.domain.org.uk. _imap._tcp 300 IN SRV 0 0 0 . _imaps._tcp 300 IN SRV 0 1 993 mail.domain.org.uk. _ldap._tcp 300 IN SRV 0 0 636 mail.domain.org.uk. _pop3._tcp 300 IN SRV 0 0 0 . _pop3s._tcp 300 IN SRV 0 0 0 . _submission._tcp 300 IN SRV 0 1 587 mail.domain.org.uk. autoconfig 300 IN A 3.10.67.19 autodiscover 300 IN A 3.10.67.19 imap 300 IN CNAME mail mail 300 IN A 3.10.67.19 smtp 300 IN CNAME mail www 300 IN A 3.10.67.19
docker-compose.yml
services:
mailserver-autodiscover:
image: monogramm/autodiscover-email-settings:latest
container_name: mail.domain.org.uk-mailserver-autodiscover
environment:
- COMPANY_NAME=My Company
- SUPPORT_URL=https://autodiscover.domain.org.uk
- DOMAIN=domain.org.uk
- IMAP_HOST=mail.domain.org.uk
- IMAP_PORT=993
- IMAP_SOCKET=SSL
- SMTP_HOST=mail.domain.org.uk
- SMTP_PORT=587
- SMTP_SOCKET=STARTTLS
restart: unless-stopped
networks:
default:
external:
name: nginx-proxy-manager
monogramm/autodiscover-email-settings
Internet Speedtest
https://github.com/henrywhitaker3/Speedtest-Tracker
Emby Media Server
https://emby.media/docker-server.html
https://hub.docker.com/r/emby/embyserver
AWS CLI
docker run --rm -it -v ~/.aws:/root/.aws amazon/aws-cli s3 ls
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/install-cliv2-docker.html
Let's Encrypt
Issue a wildcard certificate...
docker run -it --rm --name certbot -v "/usr/bin:/usr/bin" -v "/root/.aws:/root/.aws" -v "/etc/letsencrypt:/etc/letsencrypt" -v "/var/lib/letsencrypt:/var/lib/letsencrypt" certbot/dns-route53 certonly --dns-route53 --domain "example.com" --domain "*.example.com"
Check your certificates...
docker run -it --rm --name certbot -v "/usr/bin:/usr/bin" -v "/root/.aws:/root/.aws" -v "/etc/letsencrypt:/etc/letsencrypt" -v "/var/lib/letsencrypt:/var/lib/letsencrypt" certbot/certbot certificates
https://certbot.eff.org/docs/install.html#running-with-docker
VPN
OpenVPN
Server
https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/openvpn-as
Client
https://hub.docker.com/r/dperson/openvpn-client
Routing Containers Through Container
sudo docker run -it --net=container:vpn -d some/docker-container
WireGuard
ffmpeg
https://registry.hub.docker.com/r/jrottenberg/ffmpeg
https://github.com/jrottenberg/ffmpeg
https://medium.com/coconut-stories/using-ffmpeg-with-docker-94523547f35c
https://github.com/linuxserver/docker-ffmpeg
MakeMKV
This will NOT work on a Raspberry Pi.
https://github.com/jlesage/docker-makemkv
Use this in combination with ffmpeg or HandBrake (as shown below) and FileBot to process your media through to your media server - like Emby or Plex..
MakeMKV > HandBrake > FileBot > Emby
To make this work with your DVD drive (/dev/sr0) you need to have the second device (/dev/sg0) in order for it to work. I don't get it, but it works.
/root/docker/stacks/makemkv/docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
makemkv:
image: jlesage/makemkv
container_name: makemkv
ports:
- "0.0.0.0:5801:5800"
volumes:
- "/home/user/.MakeMKV_DOCKER:/config:rw"
- "/home/user/:/storage:ro"
- "/home/user/ToDo/MakeMKV/output:/output:rw"
devices:
- "/dev/sr0:/dev/sr0"
- "/dev/sg0:/dev/sg0"
environment:
- USER_ID=1000
- GROUP_ID=1000
- TZ=Europe/London
- MAKEMKV_KEY=your_licence_key
- AUTO_DISC_RIPPER=1
Troubleshooting
PROBLEM = "driver failed programming external connectivity on endpoint makemkv: Error starting userland proxy: listen tcp6 [::]:5800: socket: address family not supported by protocol."
SOLUTION = Put 0.0.0.0:5801 in the published ports line of docker compose to restrict the network to IPv4.
Docker Process Output
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 4a8b3106b00b jlesage/handbrake "/init" 40 hours ago Up 40 hours 5900/tcp, 0.0.0.0:5802->5800/tcp handbrake 89fe3ba8a31e jlesage/makemkv "/init" 40 hours ago Up 40 hours 5900/tcp, 0.0.0.0:5801->5800/tcp makemkv
HandBrake
This will NOT work on a Raspberry Pi.
Use this in combination with ffmpeg or MakeMKV (as shown below) and FileBot to process your media through to your media server - like Emby or Plex..
I have changed the port from 5800 to 5802 because Jocelyn's other Docker image for MakeMKV uses the same port (so I move that one as well to 5801 - see above).
To make this work with your DVD drive (/dev/sr0) you need to have the second device (/dev/sg0) in order for it to work. I don't get it, but it works.
YouTube / DB Tech - How to install HandBrake in Docker
Blog / DB Tech - How to install HandBrake in Docker
Docker HandBrake by Jocelyn Le Sage
Docker Image by Jocelyn Le Sage
/root/docker/stacks/handbrake/docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
handbrake:
image: jlesage/handbrake
container_name: handbrake
ports:
- "0.0.0.0:5802:5800"
volumes:
- "/home/user:/storage:ro"
- "/home/user/ToDo/HandBrake/config:/config:rw"
- "/home/user/ToDo/HandBrake/watch:/watch:rw"
- "/home/user/ToDo/HandBrake/output:/output:rw"
devices:
- "/dev/sr0:/dev/sr0"
- "/dev/sg0:/dev/sg0"
environment:
- USER_ID=1000
- GROUP_ID=1000
- TZ=Europe/London
Docker Process Output
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 4a8b3106b00b jlesage/handbrake "/init" 40 hours ago Up 40 hours 5900/tcp, 0.0.0.0:5802->5800/tcp handbrake 89fe3ba8a31e jlesage/makemkv "/init" 40 hours ago Up 40 hours 5900/tcp, 0.0.0.0:5801->5800/tcp makemkv
Automated Downloader
This takes the hassle out of going through the various web sites to find stuff and be bombarded with ads and pop-ups.
- Jackett
- Radarr
- Transmission
Jackett > Radarr > Transmission
Create a docker network which Jackett and Radarr share to talk to each other...
sudo docker network create jackett-radarr
...then continue setting up the containers below.
Jackett
Jackett works as a proxy server: it translates queries from apps (Sonarr, SickRage, CouchPotato, Mylar, etc) into tracker-site-specific http queries, parses the html response, then sends results back to the requesting software. This allows for getting recent uploads (like RSS) and performing searches. Jackett is a single repository of maintained indexer scraping and translation logic - removing the burden from other apps.
So, this is where you build your list of web sites "with content you want" ;-)
https://fleet.linuxserver.io/image?name=linuxserver/jackett
https://docs.linuxserver.io/images/docker-jackett
https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/jackett
https://github.com/Jackett/Jackett
/root/docker/stacks/docker-compose.yml
version: "2.1"
services:
jackett:
image: ghcr.io/linuxserver/jackett
container_name: jackett
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=1000
- TZ=Europe/London
- AUTO_UPDATE=true
volumes:
- ./data/config:/config
- ./data/downloads:/downloads
networks:
- jackett-radarr
ports:
- 0.0.0.0:9117:9117
restart: unless-stopped
networks:
jackett-radarr:
external: true
Radarr
Radarr is a movie collection manager for Usenet and BitTorrent users. It can monitor multiple RSS feeds for new movies and will interface with clients and indexers to grab, sort, and rename them. It can also be configured to automatically upgrade the quality of existing files in the library when a better quality format becomes available.
Radarr is the 'man-in-the-middle' to take lists from Jackett and pass them to Transmission to download.
Radarr is the web UI to search for "the content you want" ;-)
https://docs.linuxserver.io/images/docker-radarr
https://github.com/linuxserver/docker-radarr
https://sasquatters.com/radarr-docker/
https://www.smarthomebeginner.com/install-radarr-using-docker/
https://trash-guides.info/Radarr/
So, you use Jackett as an Indexer of content, which answers questions from Radarr, which passes a good result to Transmission...
- Settings > Profiles > delete all but 'any' (and edit that to get rid of naff qualities at the bottom)
- Indexers > Add Indexer > Torznab > complete and TEST then SAVE
- Download Clients > Add Download Client > Transmission > complete and TEST and SAVE
/root/docker/stacks/docker-compose.yml
version: "2.1"
services:
radarr:
image: ghcr.io/linuxserver/radarr
container_name: radarr
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=1000
- TZ=Europe/London
volumes:
- ./data/config:/config
- ./data/downloads:/downloads
- ./data/torrents:/torrents
networks:
- jackett-radarr
ports:
- 0.0.0.0:7878:7878
restart: unless-stopped
networks:
jackett-radarr:
external: true
NZBGet
Nzbget is a usenet downloader. That's all there is to say on that... even the official home page keeps things quiet.
https://hub.docker.com/r/linuxserver/nzbget
Webui can be found at <your-ip>:6789 and the default login details (change ASAP) are...
username: nzbget password: tegbzn6789
Tandoor Recipe Manager
The recipe manager that allows you to manage your ever growing collection of digital recipes.
https://docs.tandoor.dev/install/docker/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7-nb3muJxI0
/root/docker/stacks/tandoor/docker-compose.yml
version: "3"
services:
db_recipes:
container_name: tandoor_db
restart: always
image: postgres:11-alpine
volumes:
- ./data/postgresql:/var/lib/postgresql/data
env_file:
- ./.env
web_recipes:
container_name: tandoor_web
image: vabene1111/recipes
restart: always
env_file:
- ./.env
volumes:
- ./data/mediafiles:/opt/recipes/mediafiles
- ./data/staticfiles:/opt/recipes/staticfiles
- nginx_config:/opt/recipes/nginx/conf.d
depends_on:
- db_recipes
nginx_recipes:
container_name: tandoor_nginx
image: nginx:mainline-alpine
restart: always
ports:
- 80
env_file:
- ./.env
depends_on:
- web_recipes
volumes:
- ./data/mediafiles:/media
- ./data/staticfiles:/static
- nginx_config:/etc/nginx/conf.d:ro
volumes:
nginx_config:
networks:
default:
external:
name: nginx-proxy-manager
Project Send
Self-hosted file sharing... small, simple, secure.
https://docs.linuxserver.io/images/docker-projectsend
https://github.com/linuxserver/docker-projectsend
What they don't tell you in the docs is that you need a database backend - which is not in the docker compose file.
So, we just add a MariaDB database container to the stack!
Create your subdomain A record in DNS...
cli53 rrcreate domain.uk 'send 300 A 123.45.678.90'
Create your Proxy Host in Ngnix Proxy Manager with an SSL...
https://send.domain.uk
Create directories on the server for the Docker container files...
sudo -i
mkdir -p /root/docker/stacks/projectsend/data/{config,db,files}
chown -R 1000:1000 /root/docker/stacks/projectsend/data/files
/root/docker/stacks/projectsend/docker-compose.yml
version: "2.1"
services:
projectsend:
image: ghcr.io/linuxserver/projectsend
container_name: projectsend
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=1000
- TZ=Europe/London
- MAX_UPLOAD=100
volumes:
- ./data/config:/config
- ./data/files:/data
- /etc/timezone:/etc/timezone:ro
expose:
- 80
restart: unless-stopped
projectsend-db:
image: mariadb
container_name: projectsend-db
environment:
TZ: Europe/London
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: projectsend
MYSQL_DATABASE: projectsend
MYSQL_USER: projectsend
MYSQL_PASSWORD: projectsend
volumes:
- ./data/db:/var/lib/mysql
- /etc/timezone:/etc/timezone:ro
restart: unless-stopped
networks:
default:
external:
name: nginx-proxy-manager
Go to the secure web site URL and complete the installation, using the Docker container name for the 'Database hostname'.
projectsend-db
Then, log in with your Admin username and password...
- Create Group 'Public' which is public.
- Create Group 'Customers' which is not public.
- Create Client 'Customer Name' which is assigned to the 'Customers' group.
- Upload some files and test both the Public and Client links.
Enjoy.
Troubleshooting
Change the Site URL
If you move host or domain name, you can log in to the DB container and change the 'base_uri'...
docker exec -it projectsend-db bash mysql -u root -p projectsend MariaDB [projectsend]> MariaDB [projectsend]> select * from tbl_options where name = 'base_uri'; +----+----------+-------------------------+ | id | name | value | +----+----------+-------------------------+ | 1 | base_uri | https://send.domain.uk/ | +----+----------+-------------------------+
MediaWiki
Installation
Create the docker compose file and use default volume. Go to your browser at http://localhost:8080 and finish setup. Download LocalSettings.php file and copy to it to the container filesystem, then copy the whole folder to the host filsystem...
docker cp LocalSettings.php mediawiki:/var/www/html/ docker cp mediawiki:/var/www/html /root/docker/stacks/mediawiki/data/ chown -R www-data:www-data data/html chmod o-w data/html docker-compose down (then edit your docker-compose.yml file so that local folders are used) docker-compose up -d
Now, all the files are on your docker folder, ready to easily backup :-)
mediawiki
`-- data
|-- db
`-- html
~/docker/mediawiki/docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
mediawiki:
image: mediawiki
container_name: mediawiki
restart: always
ports:
- 8080:80
links:
- database
volumes:
#- ./data/html:/var/www/html <-- #2
#- /var/www/html/images <-- #1
environment:
- PUID=33
- PGID=33
- TZ=Europe/London
database:
image: mariadb
container_name: mediawiki_db
restart: always
environment:
MYSQL_DATABASE: my_wiki
MYSQL_USER: wikiuser
MYSQL_PASSWORD: example
MYSQL_RANDOM_ROOT_PASSWORD: 'yes'
volumes:
- ./data/db:/var/lib/mysql
https://hub.docker.com/_/mediawiki
Tweaks
Change default skin to mobile responsive modern one...
wfLoadSkin( 'Timeless' ); $wgDefaultSkin = "timeless";
Enable the new editing toolbar...
wfLoadExtension( 'WikiEditor' );
Make the URL shorter...
$wgScriptPath = ""; $wgScriptExtension = ".php"; $wgArticlePath = "/wiki/$1"; $wgUsePathInfo = true;
File uploads...
https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Manual:Configuring_file_uploads
https://kindalame.com/2020/11/25/self-hosting-mediawiki-with-docker/
Importing
Pages
OLD SERVER
Generate the page dump in XML format...
docker exec -it mediawiki bash php maintenance/dumpBackup.php --current > pages.xml exit
NEW SERVER
Import the pages...
cp pages.xml ./data/html/ docker exec -it mediawiki bash php maintenance/importDump.php < pages.xml php maintenance/update.php php maintenance/rebuildall.php exit
https://www.hostknox.com/tutorials/mediawiki/pages/export-and-import#import-pages-via-ssh
Images
OLD SERVER
Generate the image dumps using dumpUploads.php, which creates a txt list of all image filenames in use...
mkdir /tmp/workingBackupMediaFiles php maintenance/dumpUploads.php \ | sed 's~mwstore://local-backend/local-public~./images~' \ | xargs cp -t /tmp/workingBackupMediaFiles zip -r ~/Mediafiles.zip /tmp/workingBackupMediaFiles rm -r /tmp/workingBackupMediaFiles
NEW SERVER
Unzip the files to your container filsystem...
cd /root/docker/stacks/mediawiki unzip Mediafiles.zip -d ./data/html/
Import the Images...
docker exec -it mediawiki bash php maintenance/importImages.php tmp/workingBackupMediaFiles php maintenance/update.php php maintenance/rebuildall.php exit
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1002258/exporting-and-importing-images-in-mediawiki